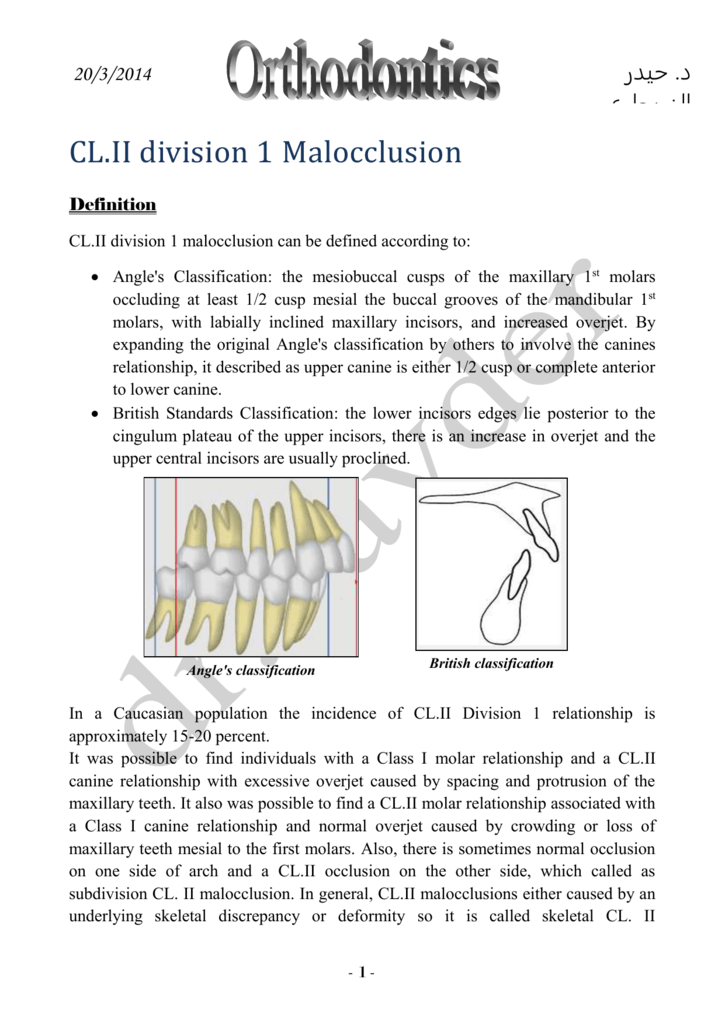
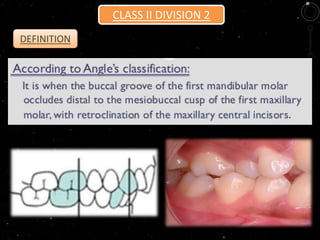
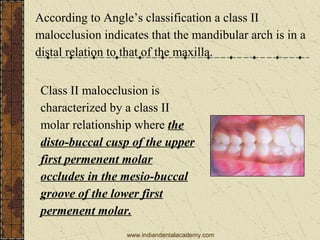
class ii malocclusion definition
Dental Arch Characteristics of Class II Malocclusions Angle 7. A class II intermaxillary dental relationship represents a posterior discrepancy of the lower teeth with regard to the upper teeth.
The maxillary first molar is inline with or anteriorly positioned relative to the mandibular first molar.
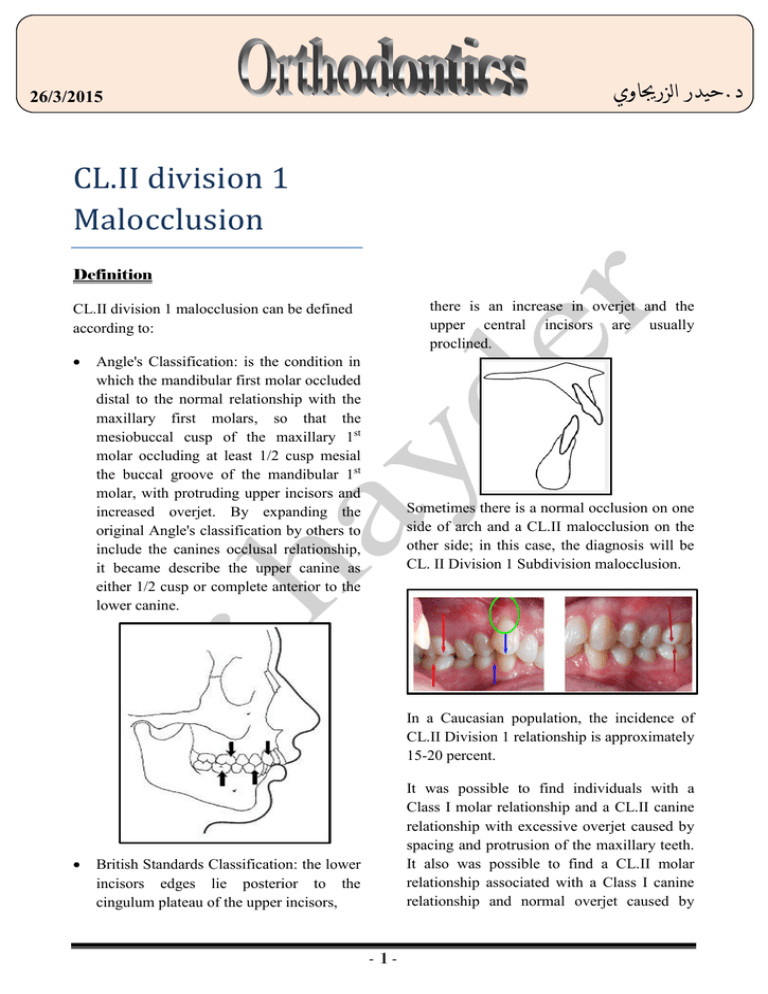
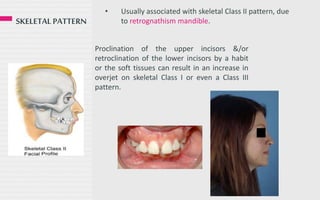
. Progressive deformity is associ-ated with mechanical limitations on growth and the resulting condition is referred to as functional 336 SPECIAL REPORT -- ETIOLOGY OF CLASS II. Class II malocclusions are generally described as having either a dental skeletal andor functional components or characteristics. Class II div 2 Dental or Skeletal combination of both 10.
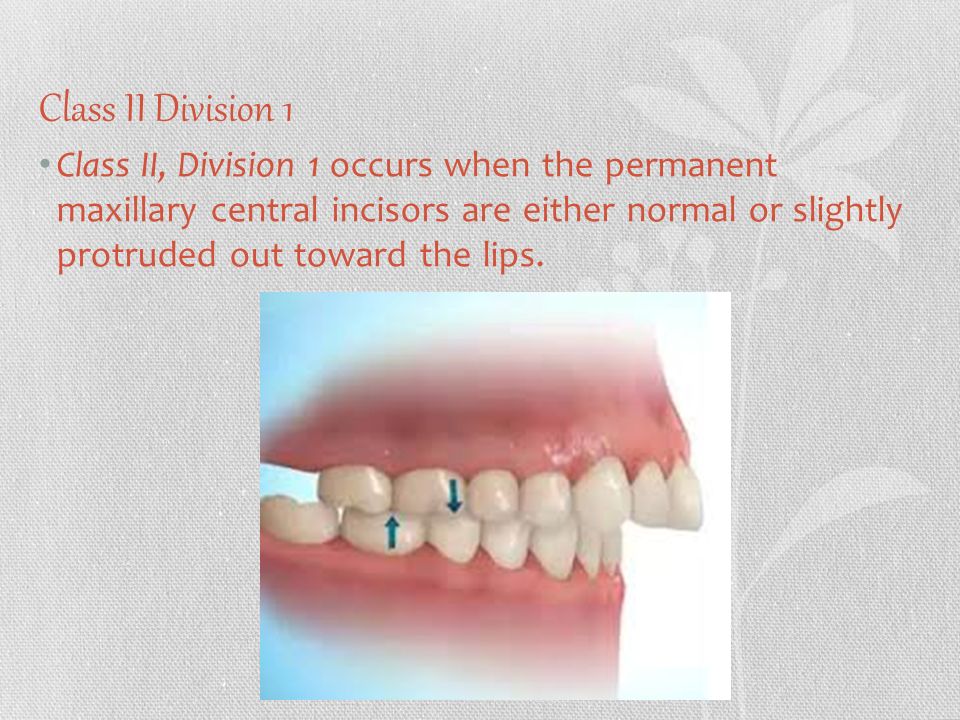
Vertical dimension in class II division 2 malocclusion is typically reduced results in absence of occlusal stop to lower incisors leading to increased overbite. The usual treatment options in growing patients. Class 2 or class II malocclusions are characterized by upper molars that are too far forward compared to the lower molars.
Class II malocclusions with asymmetry or severe mandibular deficiency. Dental malocclusions are classified based on the positioning of the upper and lower molars. Class 2 malocclusion called retrognathism or overbite occurs when the upper jaw and teeth severely overlap the bottom jaw and teeth.
Types of class 2 malocclusion Class 2 malocclusions can be subdivided into two categories division 1 and division 2. Interesting trends were noted with regard to treatment strategies midline and molar corrections and mandibular incisor proclination. Class 2 Malocclusion Distocclusion This type of malocclusion is also known as retrognathism or overbite.
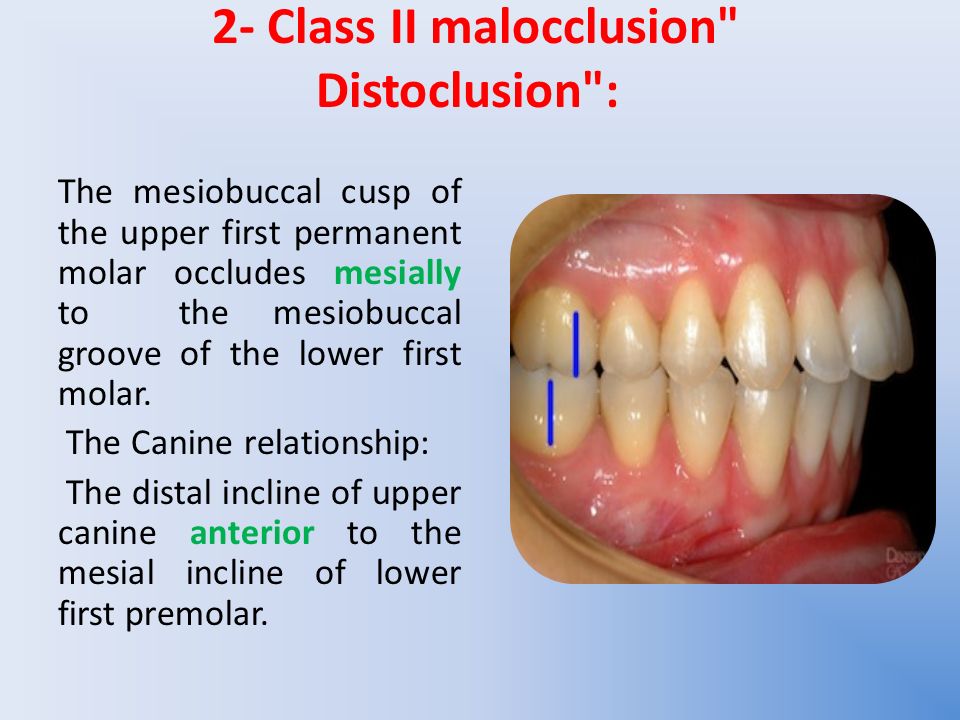
A Class II malocclusion may be accompanied by an anteroposterior skeletal discrepancy between the maxilla and mandible often with mandibular retrusion however the maxilla may also be protrusive. Class II Malocclusion A malocclusion where the molar relationship shows the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar distally positioned when in occlusion with the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar. Here are all the possible meanings and translations of the word malocclusion angle class ii.
1 Class II malocclusion may also involve craniofacial discrepancies which can be adjusted when patients are adolescent. Although these components will be discussed separately it needs to be emphasized that they are often expressed at the same time and to various degrees. These relationships are superimposed on an equally broad variation in the vertical facial pattern that ranges between increased normal or decreased.
The largest category was mandibular asymmetry. Definition of a class 1 malocclusion. The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar occluding anterior to the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar ie.
Edward Angle who is considered the father of modern orthodontics was the first to classify malocclusionHe based his classifications on the relative position of the maxillary first molar. DENTAL FACTORS Pre-existing crowding is exacerbated because retroclination of upper central incisors. Class 1 dental malocclusion is the most common type of malocclusion.
Even though sample selection based on cephalometric variables without considering the severity of the occlusal anteroposterior discrepancy is still common in current papers. Approximately 50 to 55 of children between the ages of 6 and 17 have some form of Class 1 malocclusion. Class 2 This most commonly causes a retrognathic facial profile.
A Class 2 molar relationship is described as. Class II Malocclusion Class II Malocclusion Class II Malocclusion has two divisions to describe the position of the anterior teeth. Malocclusion Angle Class II Malocclusion in which the mandible is posterior to the maxilla as reflected by the relationship of the first permanent molar distoclusion.
Class 2 malocclusion called retrognathism or overbite occurs when the upper jaw and teeth severely overlap the bottom jaw and teeth. This overbite can be caused by an overly prominent upper jaw or an underdeveloped lower jaw. It is well known that the efficacy and the efficiency of a Class II malocclusion treatment are aspects closely related to the severity of the dental anteroposterior discrepancy.
According to Angle the mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first molar should align with the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. Etiology of Class II division 2 Class II division 2 malocclusions arise from a number of interrelated dental skeletal soft tissue and genetic factors. Malocclusion Angle class II subdivision Definition A distal placement of the mandibular molar a mesial relationship of the maxillary or a combination of the two.
Terms that have commonly been associated with class II. Most of class II2 malocclusions are caused by an underlying skeletal discrepancy and few have a normal skeletal jaw relationship. National Library of Medicine 000 0 votes Rate this definition.
Definition of a class 1 malocclusion. Class II subdivision malocclusions were grouped into 3 main categories. The center of the lower first molar mesiobuccal groove is posterior to the first corner mesiobuccal cusp of.
Class II malocclusion. The teeth should all fit on a line of occlusion which in the. In this class of malocclusion either the front teeth are protruded or the back teeth overlap the central teeth.
The upper teeth and jaw overlap the lower jaw and teeth severely and the upper molars are very much anterior to the lower molars. Orthodontic Surgical Treatment For A Patient With Class Ii Malocclusion And Inadequate Maxillary Incisor Inclination American Journal Of Orthodontics And Dentofacial Orthopedics. Class II malocclusion is considered the most frequent problem presenting in the orthodontic practice affecting 37 of school children in Europe and occurring in 33 of all orthodontic patients in the USA.
Class 3 malocclusion called prognathism or underbite occurs when the lower jaw protrudes or juts forward causing the lower jaw and teeth to overlap the upper jaw and teeth. In this type of malocclusion your upper teeth and jaw significantly overlap with your lower teeth and jaw. The embrasure between the lower canine and the lower first premolar is shifted backward with regard to the upper canine blue arrows.
Class 2 malocclusion is diagnosed when you have a severe overbite. The American Veterinary Dental College defines Class II malocclusion as mandibular distocclusion when there is an abnormal rostro-caudal relationship between the dental arches in which the mandibular arch occludes caudal to its normal position relative to the maxillary arch Figure 3. A class 1 malocclusion means that the.
Definition Etiology And Treatment Of Class Ii Malocclusion
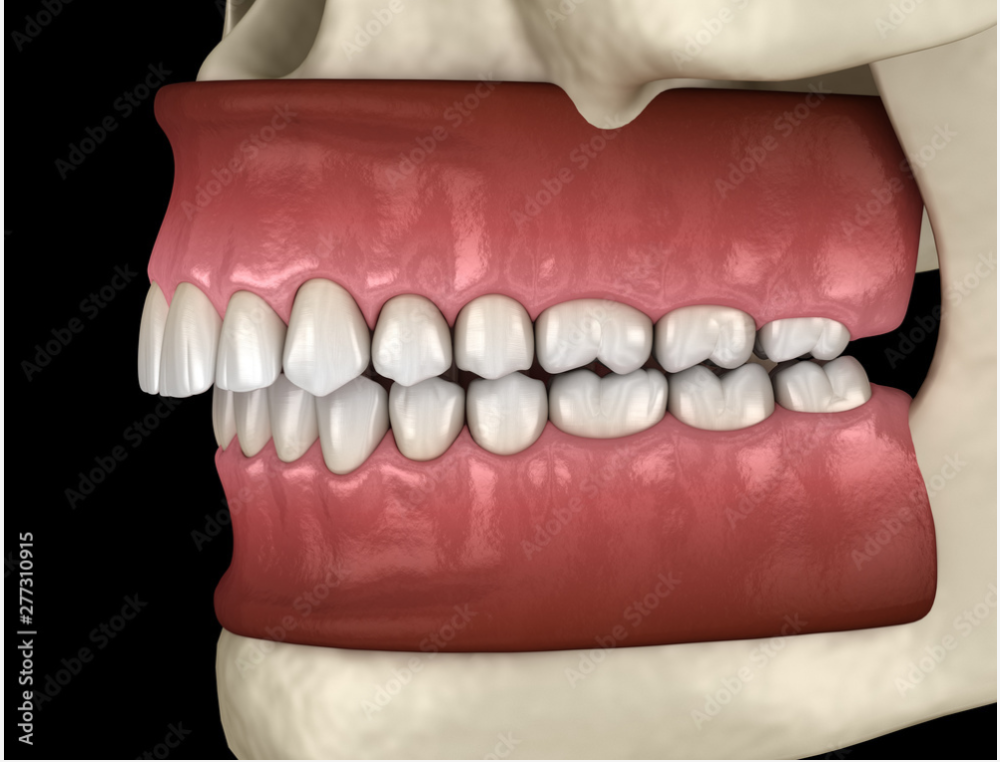
What Is A Class 2 Malocclusion Dental Information

Angle S Classification For Malocclusions Dentalnotebook

Angle Class Ii Molar Relationship For The Malocclusion To Satisfy The Download Scientific Diagram
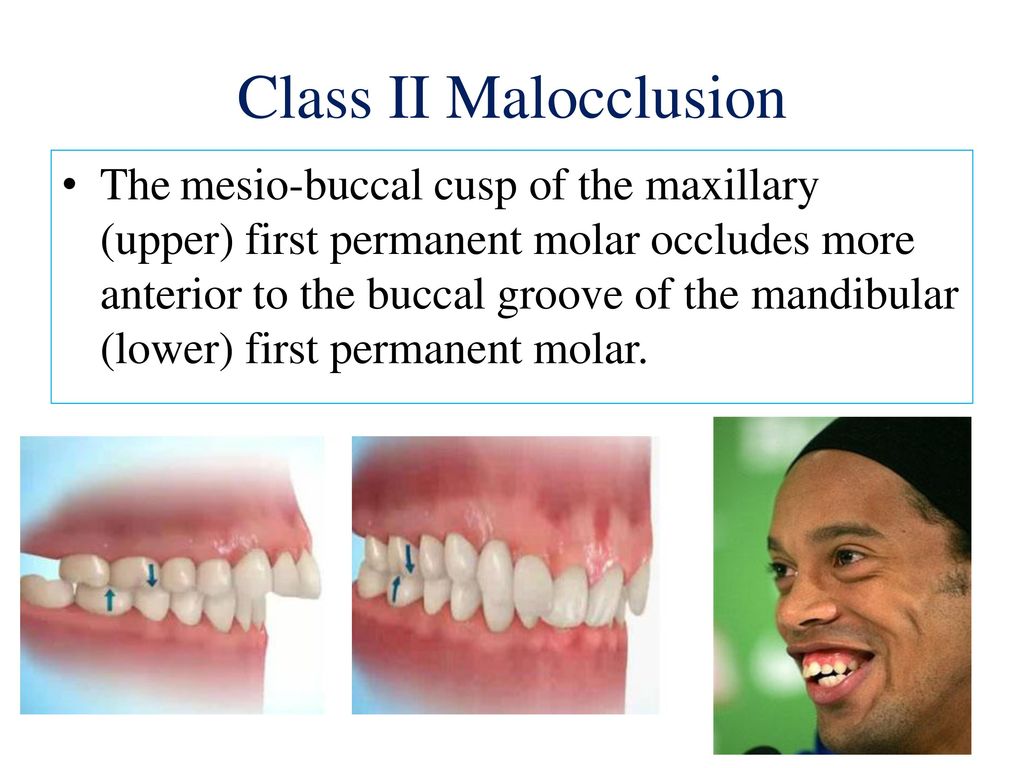
Classification Of Orthodontic Malocclusion Ppt Download
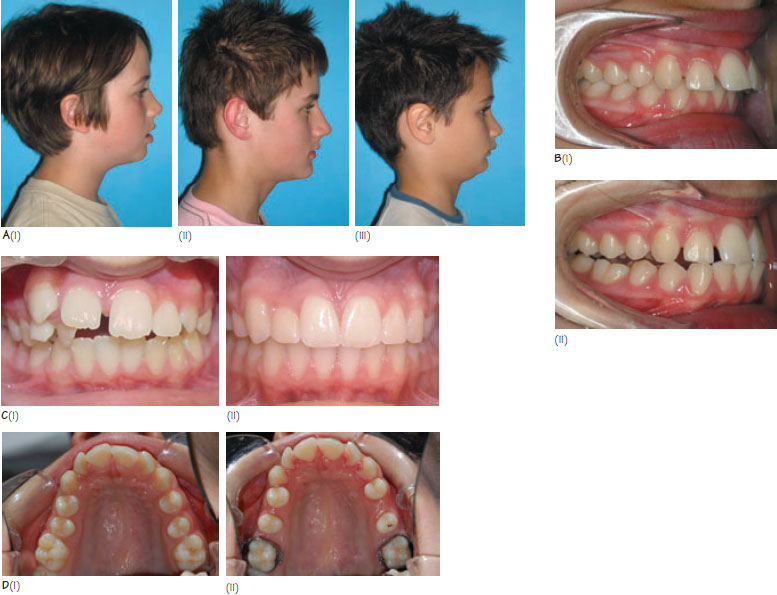
22 Class Ii Division 1 Malocclusion Pocket Dentistry
Orthodontic Dr Enas Talb 4th Class Ppt Video Online Download

Treatment Of Class Ii Malocclusions

Definition Etiology And Treatment Of Class Ii Malocclusion
Definition Etiology And Treatment Of Class Ii Malocclusion
Class Ii Malocclusion Group Ppt Video Online Download

Types Of Malocclusion And Correction Winchester Dental

Classification Of Orthodontic Malocclusion Ppt Download

Orthodontic Surgical Treatment For A Patient With Class Ii Malocclusion And Inadequate Maxillary Incisor Inclination Sciencedirect

The Aetiology Of Class Ii Malocclusion Ppt Video Online Download